News & Events
Blog post: Rail logistics: a sustainable and effective transport alternative to road haulage

22 | 03 | 2023
Logistics is of fundamental importance to the planet’s economy. Indeed, according to data from the Logistics Forum, it is calculated that there are currently over 11 million Europeans working in this sector, which accounts for over 14% of the GDP of the European economy.
Goods transport is mainly by road both in Spain and the rest of Europe. In our country alone, this accounts for 74.5% of all goods destined for domestic and overseas markets, and the figures are similar for Europe, with the environmental impact that this type of transport entails. As figures provided by the European Environment Agency reveal, road haulage is responsible for 70% of total CO2 emissions generated within the area of logistics.
In view of this data, rail has become consolidated as a sustainable and effective alternative, despite the fact that the role it plays within the transport map remains a modest one. According to data from the Transport and Logistics Observatory in Spain, it is calculated that in Spain only 1.23% – other sources put it at 4% - of goods destined for domestic and overseas markets are transported by rail.
Nonetheless, the commitment on the part of national and EU institutions to this means of transport is clear, and this seeks to cover much of the increase in logistics demand envisaged over the next few years. Specifically, Europe’s target is to ensure that rail ends up ensuring an increase from the current 18% to 30% of total logistics by 2030.
Despite the fact that rail is the means of transport with the greatest outreach, there is still a long way to go. Over the past few years, investment in innovation in terms of rail logistics has been reduced, with most investment bearing geared towards passenger transport on high-speed trains.
In contrast, other sectors such as the car industry have been applying innovative logistics solutions for a long time now, to the extent that electric self-driving lorries are just waiting for enabling technologies to enable them to embark on their activity in order to start operating in the sector.

Smart wagons for the train of the future
Within this context, the rail sector needs to become established as a more efficient alternative to be able to compete with road haulage, and it is therefore vital that both goods trains and logistics operations be digitalised. The essential area in this transformation process towards the digital train is the smart wagon, the development of which will prove to be a turning point in several areas such as: on an environmental level, as it will impact on emissions, noise pollution and energy consumption; on an operational level, it will have a positive bearing on the efficiency of processes and operations; on a logistics level, as it will favour the development of rail logistics.
In developing smart wagons, it is important to take into account the four structural elements of goods wagons – those that determine much of the efficiency of their operations.
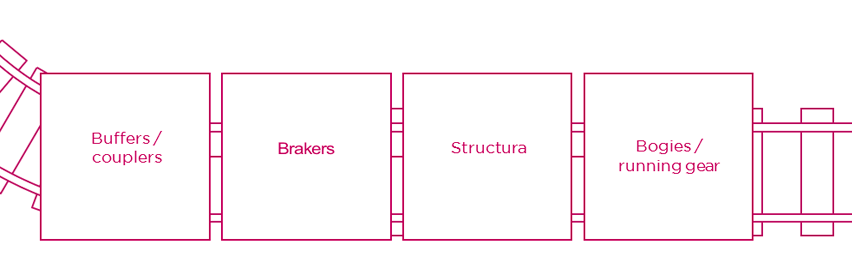
Within these elements, innovation is set to play a key role in the development and improvement of conditions regarding noise, lightness, capacity, total cost of the product throughout its life cycle costing (LCC) and, of course, in the area of logistics. It is in the case of this last-mentioned point that technology plays a leading role – above all, in four core areas:
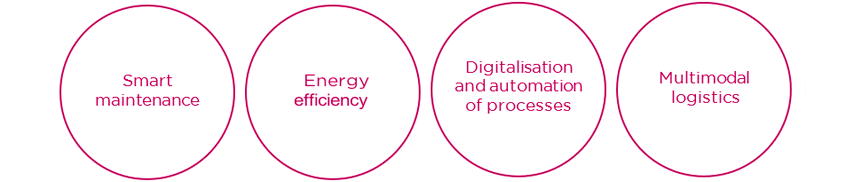
Technologies for transforming rail logistics
Different technologies need to be developed and implemented to be able to improve on these core areas. These are some of them:
| Low-cost embedded sensors | Sensor networks enable both load and smart wagon to be monitored, thus favouring predictive maintenance and even based on the conditions of the machine. |
| Positioning systems | High-precision positioning systems help to make braking and acceleration more efficient in trains, and to remove conventional train detection systems on land. |
| Wireless communications systems | Wireless communications systems such as tools that enable new technologies are required. |
| Knowledge of physical phenomena | The behaviour of the wagon and its components are modelled with a view to constructing a virtual environment (digital twins) that represents reality and enables complex scenarios to be analysed by way of predictive maintenance. |
| Electrification systems | Electrical networks or smart electrification systems help to efficiently distribute electricity among the systems in operation. |
| Data analysis | Data collection and analysis help to increase efficiency in terms of operations and optimise train maintenance. |
| Software to help in decision-making | These tools enable command-control and signalling (CSS) systems to be transformed into flexible smart traffic management systems. |
| Efficient driving | New automatic train control (ATC) systems include Grade-of- Automation 3 (GoA3) driving, bringing together efficient driving methods. |
| Integration of systems into the logistics chain | Involving all stakeholders in the use of a common platform is key to optimising processes. |
| Life cycle costing analysis | The cost/profit analysis of any innovation tends to be associated with maximising the life cycle costing of systems. |
Only research and development into these technologies together with a firm ins- titutional commitment will enable rail to become a reference point in the logistics sector, thus ensuring parameters in terms of safety, efficiency, sustainability and profitability.
For more information, you can download our free ebook about railroads:
